Dual-channel Mini Lock-in Amplifier

QTLIA is designed with the state-of-art configuration of an FPGA plus an ARM microcontroller. The floating-point signal processing is completed and optimized by FPGA hardware acceleration. The result data acquisition and host computer interaction are handled by an ARM MCU. To improve the cost performance, the system is designed for independent dual I/O channel, so that dual lock-in demodulation channel is realized on a single board, plus additional dual-channel DDS signal generations. For example, one channel can be used as a signal, and the other as a reference. Alternatively, one channel can be used for the 1st harmonic demodulation, and the other is for the 2nd harmonic demodulation.
The dual low-noise ADC samples the analog signal and converts it into two separate digital data streams, followed by the FPGA calculations. The FPGA result is sent to the ARM microcontroller for further low-speed signal processing and then the lock-in demodulation results is converted directly to the analog signal output through auxiliary DACs (AUX_DACs). Note that Moreover, a dual-channel Direct Digital Synthesizer (DDS) is used to generate two independent analog signals to two high-speed DACs that externally modulate lasers or other transmitters. All the lock-in and modulation parameters are set via a user interface installed on a PC.
Parameters
PC UI
Advantages
Technical Principle
Overall | |
Dimension | 15.4x15.4x7.6cm3 |
Weight | 670g |
Power Supply | DC 5V/2A |
Analog Input | |
Frequency | AC ~ 0.5MHz |
Input Resistance | 50 ohm |
Input Noise | 10nV/Hz1/2 (>10 kHz) |
Voltage | -1V to +1V |
ADC | 14 bit; 4 MSa/s |
DDS Analog Output | |
Output | 2 channels; -1V to +1V |
Frequency | DC ~ 0.5MHz |
DAC | 16 bit; 4 MSa/s |
Lock-in Demodulator | |
Number of Demodulators | 2 |
Time Constant | 10ms, 100ms (customizable) |
Filter Bandwidth (Hz) | 1000, 100 (customizable) |
Harmonic | 1F, 2F, 3F, 4F |
Reference Phase Resolution | 1.0 degree |
Auxiliary Output (AUX_DAC) | |
Output Channels | 2 channels; -10V to +10V |
DAC | 16 bit; 4 Msa/s |
DAC Analog Bandwidth | 10 kHz |
Host Port | USB virtual serial port |
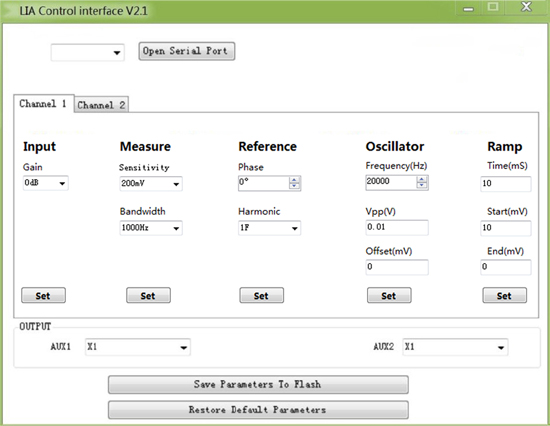
◇ Internally synchonized reference frequency that avoids an external reference signal input;
◇ Demodulation down to 10nV, with weak signal of center frequency 500kHz;
◇ Two independent inputs to realize dual-channel lock-in demodulation;
◇ Two DDS modulation outputs with adjustable frequencies, amplitudes and offsets;
◇ Two low-speed auxiliary analog channels that provide real-time lock-in demodulation results;
◇ USB virtual serial port to connect the host computer that provides a simple UI to control;
◇ Small size, good portability and usefulness for system integration;
◇ Flexible customization of FPGA algorithms upon user requirements.
Lock-in amplifiers use PSD (Phase Sensitive Detector), a phase-sensitive detecting technology. Only signals at a specific reference frequency can be selected. Noise and interference signals at other frequencies are not detected. It is a highly sensitive data acquisition device for detecting very weak AC signals. Accurate measurement can be ensured even when the noise is several thousand times stronger than the signal.
Traditional lock-in amplifiers use analog frequency mixers and RC filters for the demodulation. Complicated analog circuit designs and optimization for analog signal demodulation are indispensable. Today, lock-in amplifiers have been transformed to adoptadvanced integrated circuit technology and fast digital signal processing (DSP), increasing their sensitivity and reliability by hundreds of times.
